Can Cats See in the Dark in Boston, MA?
For years, cats have been known to have extraordinary vision. Cats can see six times better than humans in low light conditions and at night. Cats also have a wider field of view than humans. Scientists believe that cats’ eyesight has evolved to help them survive in the wild, so it isn’t farfetched to learn that cats can see in the dark.
Cats can see in the dark because they have a reflective layer at the back of their eye, which reflects light through the retina a second time. This allows them to make the most of dim light conditions and ensures they can see clearly, even when there isn’t much light to work with.
The reflective layer in human eyes (known as the tapetum lucidum) isn’t nearly as effective as in cats’ eyes. That’s why cats can see in near-darkness, and we can’t. Keep reading if you want to know more about how and why cats can see in the dark.
The Nocturnal Cat
Cats are nocturnal animals, which means they are active at night. Cats have better night vision than humans and most other animals, which is attributed to adaptation to their night-time lives. They get to see in the dark because their eyes have an abundance of rods, which are more sensitive to light than cones. This means that a cat will have a better chance of seeing in the dark than humans or other animals in a dark room.
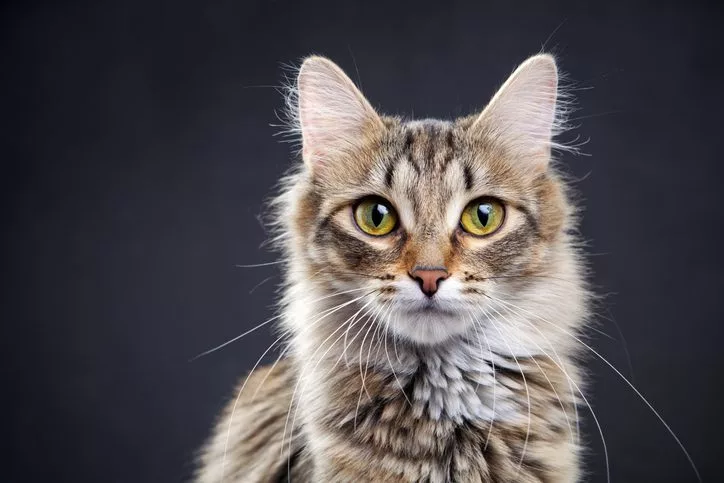

How Do Cats See in the Dark?
Cats have a layer of cells called the tapetum lucidum which reflects light up to the retina. This allows cats to see in the dark by reflecting light off their retina back to the eye. This same reflective layer also causes cats to have a “yellow-green” glow when in the dark. The shape of the eye also gives them superior night vision and the ability to distinguish between different objects.
The Science Behind the Eyes
To see in the dark, a cat’s eyes contain many cells sensitive to light. These cells are found in the retina of the eye. They are called rod cells. Cats also have a second type of eye cell called a cone cell. These cells are found in the center of the retina, and they help a cat see colors. Cats have three types of cones which are blue, green, and red. This gives cats vivid color vision. Cats also have another type of eye cell called a double cone cell. These cells are found in the fovea in the retina’s center, and they help a cat see in dim light.
Unique Eye Structure
Cats have very good night vision and can see in the darkest of the dark. They have a one-of-a-kind retina with more rods than cones, a combination that gives them the ability to see in the dark and to possess a wide field of vision. Cats have a more complex eye structure than humans, and this benefits them greatly in various ways.
Benefits of Night Vision for Cats
Cats are nocturnal creatures and hunters of prey that is active at night. Seeing well in the darkness benefits cats because they can hunt when most other animals are asleep. The ability to see in the dark is a natural ability that helps cats hunt, find prey, and navigate their way through the world.
The Third Eyelid
Cats have a third eyelid that sets them apart from humans or other animals like dogs. A cat’s nictitating membrane, or third eyelid, serves many purposes. It helps to protect the eyes from dust, dirt, and debris. The reflective layer of the membrane also allows cats to see better in low light conditions.
Other Structural Aspects
Because cats’ eyes are on the sides of their head, they have a much wider field of vision than we do. They have superior night vision, can see near-total darkness, and perceive colors in dim lighting. Cats have binocular vision, meaning they can see from side to side, not just up or down like humans.

Cat’s See in a Different Spectrum: The UV Spectrum
Cats can see in the dark due to an adaptation of the retinal cells in their eyes. Retinal cells can absorb light that is not visible to humans. Cats can see in various wavelengths but mainly in the ultraviolet (UV) spectrum. The UV spectrum is achieved through the cat having transparent lenses that don’t deflect UV light.
How Dark is Too Dark?
They can’t see in total darkness, but they are pretty close to it because their pupils are shaped like vertical slits, not circular ones like humans. This allows the cat’s eyes to let in more light and focus on nearby objects better in low-light and dim conditions. Yet, a cat cannot see in total darkness any better than any other animal or a human because the light is needed, even in very minute amounts, for an image to be reflected somewhere in the eye.
A Good Diet Keeps Their Vision In Great Shape
It is essential to make sure your cat has a well-balanced diet to help them maintain its fantastic senses. Having the proper nutrients and vitamins in their diet supports their ocular health and allows their bodies to work better for longer.
Conclusion
Cats have fantastic night vision that is the result of several adaptations. For example, cats have a tapetum lucidum. This reflective layer of tissue behind the retina helps them see in low light conditions. They have a tapetum lucidum, a layer of tissue that reflects light in such a way that it acts as a mirror. The tapetum lucidum is a reflective layer of tissue that helps cats see in low-light conditions. This is because the tissue reflects light into the eye, amplifying it and making it easier to see in dim lighting. While cats sleep, a third eyelid called a nictitating membrane protects their eyes from dirt and debris.
If you have any questions or would like to schedule an appointment for your pet, call us at (617) 245-2710 or make an appointment online! We look forward to hearing from you!
Recent Posts
- « Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next »